

Here, we have the hop number (1), the domain name/IP address (in this case a home router), then RTT1, RTT2, and RTT3 (Round Trip Time - the time it takes for a packet to get to the hop and back to the. that we arnt getting a response from a DHCP server ). 1 homerouter.cpe (192.168.8.1) 10.129 ms 1.528 ms 1.373 ms.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/2019-03-19_16h09_50-5c914cb946e0fb0001770166.png)
I can see above, the DHCP discover packets have been parsed correctly (and. Now the output is ready for you to analyse: If you do not have the process ID available from when the trace was started, issue ps -ef grep iptrace to obtain the process ID ( pid ). You need the process ID to stop the trace process. When you open the file you might find that it looks a bit rubbish at first:Īll you need to do is go to the tools > options tab so that you can tell netmon which parsers to use to convert the trace:Ĭhoose the Windows parsers and dont forget to click "set as active" before you click OK or nothing will happen. When iptrace is started from a command prompt, the process ID is written to the terminal and the trace runs in the background. For customers, I capture using the netsh switch then get permission to view the data on my machine where I have netmon installed. Now that you have the trace, you can take it to a machine where installing netmon is more appropriate to view the data. If you forget to elevate the prompt you will get this: Log on and stop the trace using: " netsh trace stop" (from an elevated prompt). I will do this trace for a slow boot scenario - it works fine for non reboot scenarios too, just reproduce the issue and then stop the trace.ģ. You can view the trace on another machine using netmon. Your trace will be stored in c:\temp\nettrace-boot.etl**or where ever you saved it. Open an elevated command prompt and run: " netsh trace stop" Reproduce the issue or do a reboot if you are tracing a slow boot scenario.ģ. Open an elevated command prompt and run: " netsh trace start persistent=yes capture=yes tracefile=c:\temp\nettrace-boot.etl" (make sure you have a \temp directory or choose another location).Ģ. (This feature works on Windows 7/2008 R2 and above).ġ.
#IPTRACE WINDOWS CMD INSTALL#
For example in Ubuntu the command to install trace route is “sudo apt-get install traceroute”.If you need to capture a network trace of a client or server without installing Wireshark or Netmon this might be helpful for you. To perform a trace route in Linux open Terminal and type in “traceroute ” replacing with your domain name or IP address. If you do not have trace route installed you may need to install it. Once open, type in “traceroute ” replacing with your domain name or IP address. On computers running Windows Server® 2012 and Windows® 8, you can use the Netsh Trace context from a command prompt to enable and configure network tracing to assist you when troubleshooting network connectivity problems. You can open Terminal by going to “Applications” in finder, then “Utilities” and double clicking on “Terminal”.
#IPTRACE WINDOWS CMD UPDATE#
Step 4: Run Windows Update again using the above mentioned methods. Step 3: Delete all the files from the above mentioned folder. This folder contains all the update files that Windows Operating System is currently downloading or recently downloaded and installed.
#IPTRACE WINDOWS CMD MAC#
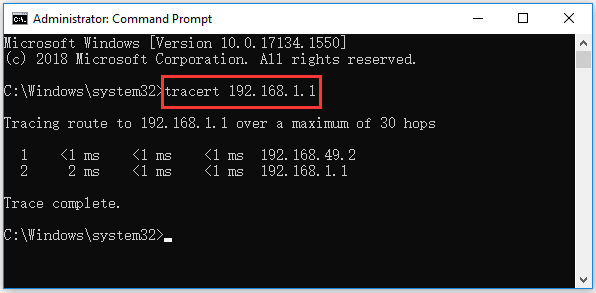
To perform a trace route in Mac you need to open Terminal. Step 2: Open C:WindowsSoftwareDistributionDownload. Replace with your domain name or IP address. In this post, I’ll provide a quick overview and some advice on configuring the extension, and then I’ll share some resources so you can learn more. Command prompt should display a black box in which you can type the command “tracert ”. Figure: Windows Terminal + PowerShell Running EF Core CLI The quickest and most productive way to open Windows Terminal in Visual Studio is to use the Open Command Line extension. You are safe to close the Command Prompt window now. For more information about using the IP trace functions, see IBM Tivoli NetView for z/OS IP Management. The types of traces are component trace (CTRACE), IP packet trace (PKTTRACE), and OSA packet trace (OSATRACE). You can perform a traceRoute in Windows Vista, Windows 7 and above by opening the “Start” menu to find the search field. txt should be created on your desktop that contains the tracert results. The IPTRACE command is used to perform diagnostic traces to help resolve TCP/IP problems. TraceRoute shows you the route (path) that was used to connect you to the IP address or hostname.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
